One of the most powerful features of the EMME/2 auto assignment is certainly the additional options analysis. It provides a very general framework to compute volume and matrix results pertaining to a well defined class of paths only. The applications of the additional options assignment are innumerable; they range from simple select link analyses to complex demand matrix adjustment models. Up to now the analyses possible within the additional options framework were always limited to select or reject complete paths, which implies that a path is either included in the slave assignment in its entity from origin to destination, or is excluded all together.
There are, however, many interesting problems in which only a part of the path from the origin to the destination is of interest. Consider for example the effects of cold starts on the emission of pollutants. During the initial part of the path, when the engine is still cold, the fuel burning conditions are not optimal and the catalyst is not yet working efficiently, so that during this phase of the trip additional emissions are generated. Often the effect of cold starts are modeled in a simplified manner by assuming that they occur only at the origin node. Knowing the partial volumes which correspond to this initial ``cold start'' portion of the trip would allow the implementation of more precise models which distribute the cold start emissions along the street links on which they actually occur.
In order to extend the concept of additional options to answer
questions of the type described above, a new special path operator
``cutoff'' has been introduced. When this path operator is
chosen, the additional options assignment will retain only volumes
that occur on the selected part of the path. The retained part
is defined by the additional link attribute, which serves as the ``distance''
measure along the path, and the lower and upper path threshold values.
Note that the term ``distance'' is used here in a general sense as
the sum of the additional attribute values along the path ( only if
using length as additional link attribute does this correspond
to the ``true'' distance).
The lower
threshold value defines the distance where the selected part of the path
begins, whereas the upper threshold value defines the distance along the
path where the selected part ends. Both beginning and ending distances
can be defined either as distance from the origin (>0) or to the destination
(<0). A zero value for the lower threshold implies the origin (+0), whereas
a zero for the upper threshold value implies the destination (-0).
Since the beginning and ending points of the retained part of the path
do not, in general, coincide with a network node, on links which are
only partially retained the additional demand is assigned on a pro-rata basis.
No volume is assigned if the path segment between the beginning and ending
points is empty. The additional path attribute, which can be saved in
a matrix, corresponds to the length (as defined by the distance measure)
of the retained part of the path.
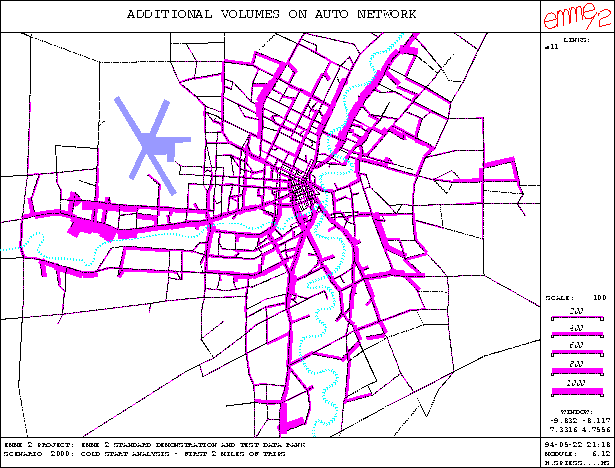
To return to the example of cold starts, let us assume that the
effect of the cold start is limited to the first two miles of the trip.
The corresponding partial volumes can be obtained using the new cutoff
path operator with length as the additional link attribute and
the threshold values (0,2). The resulting additional volumes are shown
below for the standard Winnipeg demonstration data base. As one might
expect for a morning peak, the effect of the cold starts occur mainly
along the major arteries approaching the CBD, while in the city center
the effect is only minimal.

We conclude this discussion outlining two other examples for possible
applications of the cutoff operator:
cutoff operator now opens the possibility for applying
a more precise distinction criterion in which a vehicle is considered local when
closer than a certain distance to either origin or destination zone,
and regional otherwise. Using the additional link attribute length
with the threshold values (+3,-3) would produce additional volumes
which correspond to the regional part of the trips, i.e. vehicles which
have already traveled more than 3 kilometers from their origin
and still have more than 3 kilometers to go until they reach their
destination.cutoff operator and the threshold values (1,-1), will allow the
computation of the ``observable'' part of the volumes, i.e. the parts
of the paths contained between the licence plate observation points.